Table of Contents
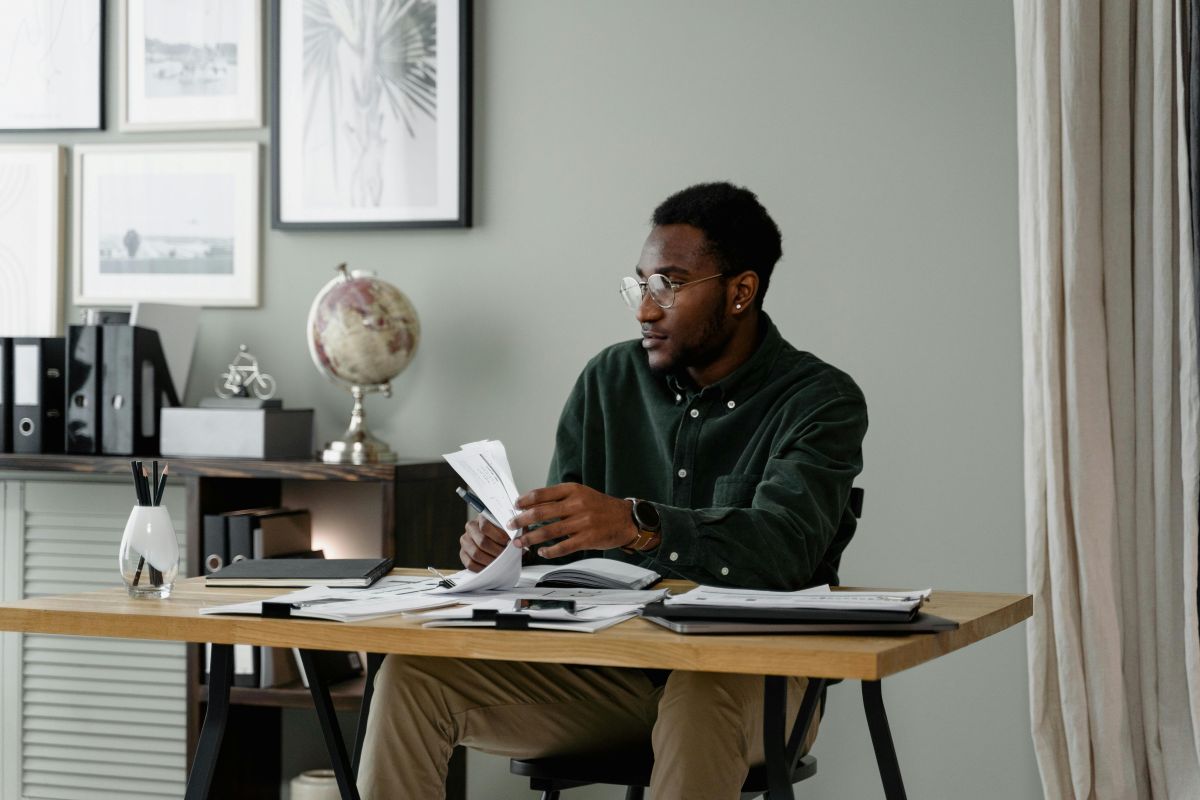
ToggleJapan’s IT industry, valued at billions of dollars annually, is a critical driver of innovation, efficiency, and growth across sectors such as manufacturing, healthcare, and finance. Renowned for its advancements in artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and cybersecurity, the industry is pivotal in shaping the country’s digital transformation and global competitiveness.
Key Players and Industry Structure
Japan’s IT industry is diverse, comprising major multinational corporations, startups, and government-driven initiatives. Key players include Fujitsu, NEC, Hitachi, and Sony, alongside global tech giants like Microsoft, Google, and Amazon, which have significant operations in Japan.
The ecosystem also includes a burgeoning startup scene, supported by government initiatives such as the “Digital Garden City Nation” project, which fosters regional innovation. Collaboration between established corporations and startups has fueled the development of cutting-edge solutions in artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and cybersecurity.
Technological Advancements
Japan’s IT industry has been at the forefront of numerous technological breakthroughs. Some of the key advancements include:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI plays a transformative role in sectors like healthcare, manufacturing, and finance. Japanese companies are leveraging AI for applications such as predictive analytics, robotic process automation, and natural language processing. For instance, AI-driven robots are revolutionising manufacturing by enhancing productivity and precision and Japanese airlines use predictive analytics to prevent delays.
2. Cloud Computing
Cloud adoption in Japan has grown exponentially, with businesses embracing services that enhance scalability and flexibility. Major cloud providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure dominate the market, while domestic firms like NTT Communications offer tailored solutions for local businesses.
3. Cybersecurity
As digital transformation accelerates, cybersecurity has become a top priority. Japan’s IT industry has developed robust solutions to counter cyber threats, including advanced firewalls, threat detection systems, and secure data management platforms.
4. IoT and Smart Solutions
Japan is a leader in IoT applications, integrating smart technologies across sectors like agriculture, logistics, urban planning, and manufacturing. IoT-driven advancements are transforming industries by enabling real-time data collection, predictive analytics, and automation.
- Smart Agriculture: IoT sensors monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health, optimising irrigation and fertilisation to increase yields and reduce resource waste.
- Logistics: IoT-powered tracking systems provide real-time updates on shipments, improving supply chain efficiency and reducing delays.
- Urban Planning: Smart city projects in Tokyo and Osaka use IoT to manage traffic flow, reduce energy consumption, and enhance public safety through connected streetlights and surveillance systems.
- Healthcare: Wearable devices and remote monitoring systems enable better patient care by collecting and analyzing health data, assisting doctors in making informed decisions.
These applications not only enhance efficiency but also improve quality of life and environmental sustainability, showcasing Japan’s leadership in leveraging IoT for societal benefits.
The Role of Government and Regulation
The Japanese government has played a pivotal role in fostering IT growth through policies and investments. Initiatives like “Society 5.0” aim to create a human-centered society powered by digital innovation. Additionally, deregulation in the IT sector has encouraged foreign investment and enhanced market competition.
Challenges Facing the Industry
Despite its strengths, Japan’s IT industry faces several challenges:
- Aging Workforce: The industry struggles with a declining population and a shortage of skilled IT professionals.
- Global Competition: Japan competes with countries like the United States, China, and South Korea, which are advancing rapidly in AI and other technologies.
- Slow Digital Adoption: Some traditional industries have been slow to adopt digital transformation, limiting the IT sector’s domestic growth potential.
Opportunities for Growth
The future of Japan’s IT industry lies in addressing these challenges and capitalizing on emerging opportunities:
- Reskilling and Education: Investing in IT education and upskilling programs can address workforce shortages.
- Green IT: Developing energy-efficient technologies aligns with global sustainability goals and opens new markets.
- Cross-Border Collaboration: Strengthening partnerships with global tech leaders can enhance innovation and competitiveness.
Conclusion
Japan’s IT industry continues to be a global powerhouse, driven by innovation, government support, and collaboration. By addressing current challenges and embracing opportunities, the industry is well-positioned to lead the next wave of digital transformation, both domestically and internationally. As Japan moves towards its vision of a tech-driven Society 5.0, its IT sector will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future.
Eos has over 15 years of experience serving the Japanese market. Check our services here or book a free consultation now.